This week brought several meaningful updates across Google Search, AI-driven experiences, and web crawling behaviour, each signalling how quickly the search landscape is evolving. Google continues to blur the boundaries between traditional search and AI Mode, quietly testing new interfaces and introducing subtle changes that could reshape user discovery paths.
Meanwhile, OpenAI is scaling its crawling infrastructure, accelerating the race to build more informed large language models. Combined with new data on AI citation factors and changes in how platforms manage content inputs, it’s clear that search is moving firmly toward an AI-first era. Here are the major updates of the last week.
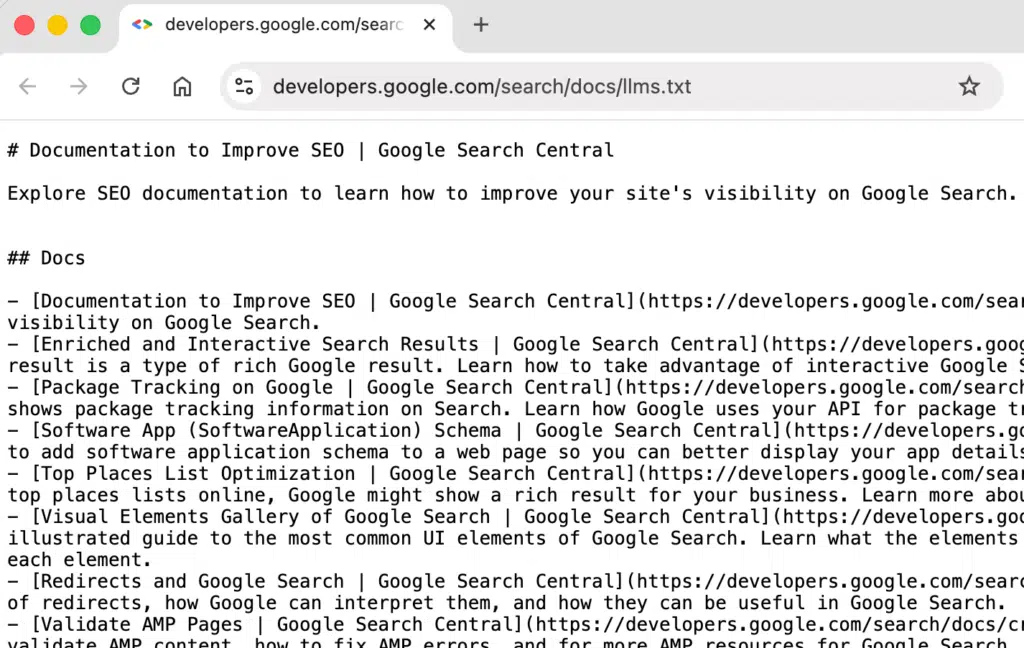
1. Google Adds “llms.txt” to Its Official Developer Docs
What happened:
Google unexpectedly added a file named llms.txt to its Search Central developer documentation site, despite previously stating the file was unnecessary. This has generated confusion and speculation across the SEO community.
The file is over here: developers.google.com/search/docs/llms.txt. Here is a screenshot:
Here is Barry Schwartz post:
Whoa – Google Search Central added an LLMs.txt file to its portal www.seroundtable.com/google-adds-… via @lidia-infante.com with a response from @johnmu.com #google #seo #llmstxt
— Barry Schwartz (@rustybrick.com) December 3, 2025 at 5:51 PM
[image or embed]
Why it matters:
The presence of llms.txt on Google’s own domain suggests Google may be testing or preparing for future standards on AI crawler governance.
What to do:
- Treat this as exploratory; Google has not officially adopted llms.txt as a standard.
- Monitor updates; if Google formalises its use, SEOs may need to publish their own llms.txt file.
- Maintain focus on core SEO quality signals until clearer guidance emerges.
2. Google Begins Blending AI Mode Into AI Overviews
What happened:
Google is testing a “Show more” button inside AI Overviews that opens directly into AI Mode, effectively merging both search experiences into a single flow.
Why it matters:
This reduces friction for users switching from a summary to a full conversational search session. It could further reduce traditional organic clicks as more answers happen inside AI Mode.
What to do:
- Ensure content is clear, expert-backed, and easily summarizable.
- Track queries where your content appears in AI Overviews.
- Prepare for lower click-through as AI answers absorb more informational intent.
3. Google Adds Image Upload Button to the Search Bar (AI Mode Trigger)
What happened:
Google’s desktop search bar now shows a “+ upload” button that lets users submit images or files directly, and this automatically triggers AI Mode rather than standard search.
Google looks to have now launched an image and file upload icon attached to their homepage on desktop by default in the US.
— SERP Alert ⚡️ (@SERPalerts) December 3, 2025
When uploading a file, entering the search takes the user directly to AI Mode. The expectation here is that adding a file assumes that AI Mode is a more… pic.twitter.com/WjhIiCUfMc
Why it matters:
More users are being funneled into AI Mode by default, especially for image-based or document-based queries. This may reduce Google Images traffic and change how discovery paths work.
What to do:
- Optimise visual content with descriptive metadata, alt-text, and structured context.
- Review image-based traffic for shifts caused by AI Mode.
- Ensure documents (PDFs, guides, manuals) are structured for AI parsing.
4. OpenAI Greatly Expands Its Crawl Bots (AI Indexing Surge)
What happened:
OpenAI has broadened its crawling infrastructure with new IP ranges for more aggressive scraping ahead of the holidays.
Why it matters:
AI crawlers are indexing more content than ever. AI visibility, being cited in model responses, is becoming a new form of discoverability.
What to do:
- Check server logs to ensure OpenAI crawling isn’t straining resources.
- Strengthen site structure, metadata, and internal linking for AI readability.
- If needed, use robots.txt or firewall rules to manage OpenAI crawler access.
5. New Data Reveals Top Factors Behind ChatGPT Citations
What happened:
SE Ranking study analysing over 200,000 pages found that ChatGPT citations strongly correlate with domain authority, backlink volume, topical expertise, content depth, and freshness.
Why it matters:
AI engines increasingly pull from authoritative, well-linked, and comprehensive sources. SEO signals still matter, now for AI, not just search engines.
What to do:
- Prioritize authority building (backlinks, digital PR, expert content).
- Publish long-form, deeply researched content.
- Refresh older content to maintain AI relevance.

Ridam Khare is an SEO strategist with 7+ years of experience specializing in AI-driven content creation. He helps businesses scale high-quality blogs that rank, engage, and convert.



