Every time you type a question into Google or search for a product online, you’re witnessing search and indexing in action. But have you ever wondered what’s actually happening behind that search box? How do search engines know exactly what you’re looking for within seconds? It’s not magic – it’s a fascinating process of crawling, indexing, and ranking that powers our digital world.
Let’s pull back the curtain and explore how search engines work their magic, from discovering content to delivering the perfect results for your queries.
The Diverse World of Search Engines: Types and Functions
Traditional Search Engines
When most of us think about search engines, we picture Google, Bing, or Yahoo. These traditional search engines cast a wide net across the entire web, processing billions of pages to create massive, general-purpose indexes. They’re designed to handle any query you throw at them, from “best pizza near me” to “quantum physics explained.”
These engines use complex algorithms that analyze hundreds of factors to match your query with the most relevant results. Google, for instance, processes over 8.5 billion searches every single day!
Source: Statcounter
Vertical or Search Specific Engines
Unlike their all-purpose cousins, vertical search engines focus on specific types of content or industries. Think about:
- Amazon – for products
- YouTube – for videos
- Zillow – for real estate
- LinkedIn – for professionals and jobs
These specialized engines tailor their indexing and ranking systems specifically for their content type. Amazon’s search cares about different signals than Google does – like sales history, reviews, and inventory status.
AI Powered Search Engines
The newest kids on the block are AI-powered search engines like Perplexity, ChatGPT, and the AI features in traditional search engines. These tools use machine learning to better understand context and intent, often providing direct answers rather than just links.
AI search can grasp nuance and complexity in ways traditional algorithms couldn’t. They can understand natural language, detect sentiment, and make connections between concepts that would have previously been missed in indexing.
“AI is going to be the most significant change for the industry now and in the future. But you have to take the attitude of – Alright, AI is here, and it might change search results in a big way, and it might change how I do my job, but you have to be one of the first to adopt it.”
-Barry Shwartz
How Search Engines Work (Step-by-Step)
Crawling
Search and indexing begin with discovery. Search engines use programs called “crawlers” or “spiders” (like Googlebot) that constantly explore the web by following links from page to page. Think of them as tireless digital explorers mapping every corner of the internet.
When crawlers find a page, they read its content and follow links to discover new pages. This process happens continuously, with billions of pages being crawled daily. Not every page gets crawled with the same frequency – popular sites might be visited multiple times a day, while less active sites might only see a crawler once a week.
Indexing
After crawling comes indexing – the heart of how search engines work. During this process, search engines:
- Process and analyze page content, including text, images, videos, and more
- Extract meaning from the content to understand what it’s about
- Store this information in enormous databases (the index)
- Organize everything to enable lightning-fast retrieval
Indexing in SEO is crucial because if a page isn’t indexed, it simply doesn’t exist to the search engine. No indexing means no chance of ranking, no matter how great your content is.
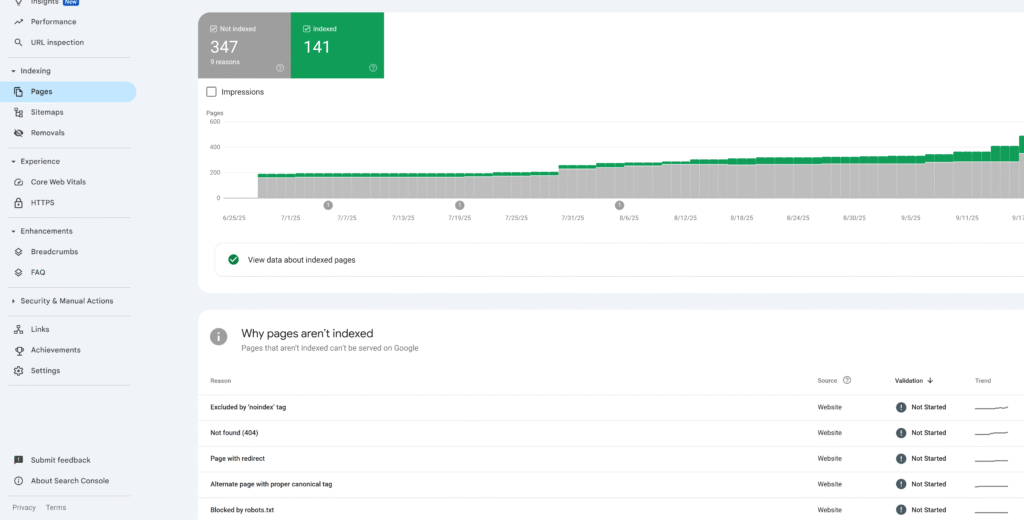
Indexing Report in Google Search Console
Ranking
Once pages are indexed, they can be ranked. Ranking is where search engines determine which pages to show for a specific query and in what order. This is where the real competition happens!
How engines rank and serve results
What factors influence ranking?
Search engines use hundreds of signals to rank pages. Some key factors include:
- Relevance: How well does the content match the search query?
- Authority: Does the site have credibility on the topic?
- User experience: Is the page fast, mobile-friendly, and easy to use?
- Content quality: Is the information valuable, accurate, and comprehensive?
- Freshness: Is the content up-to-date?
How search engines process indexed pages
Once pages are in the index, search engines continuously update their understanding of them. They note changes in content, monitor how users interact with the pages, and adjust rankings accordingly.
The index isn’t static – it’s constantly evolving as web crawlers bring in fresh data. Pages can gain or lose positions based on new content, changing user behaviors, and updates to the search algorithm itself.
What happens during query matching?
When you type a search, here’s what happens in milliseconds:
- The search engine analyzes your query to understand your intent
- It searches its index for relevant content
- It ranks the matching results based on hundreds of factors
- It personalizes results based on your location, search history, etc.
- It displays the results, often with snippets of relevant information
This entire process happens so quickly you barely notice it – but the technology behind it is incredibly sophisticated.
Summing up how search and indexing work
Search and indexing form the backbone of how we access information online. From crawling the vast web to processing and organizing content, and finally matching it perfectly with user queries, search engines perform an incredible balancing act of technology.
Understanding these processes helps us appreciate the complexity behind that simple search box. For website owners and content creators, this knowledge is even more valuable – it’s the key to making your content discoverable in an increasingly crowded digital landscape.
FAQs
How does indexing in SEO impact rankings?
Indexing is the foundation of SEO – without it, your content simply can’t rank. Good indexing practices ensure search engines understand what your pages are about. This includes using clear site structure, proper HTML markup, quality content, and a good internal linking strategy. Problems with indexing often cause ranking issues, so monitoring your indexed pages through Google Search Console is essential for SEO success.
What is the role of web crawlers in search engines?
Web crawlers serve as the discovery mechanism for search engines. They find new and updated content by following links across the web, read and process page content, and send that information back to the search engine for indexing. Without crawlers, search engines would have no way to find or update content in their index. You can help crawlers by having a clean site structure, using sitemaps, and ensuring your robots.txt file doesn’t accidentally block important content.
How does Google decide which pages to show first?
Google uses a complex algorithm with hundreds of factors to decide page rankings. The most important include content relevance to the query, page loading speed, mobile-friendliness, authority signals like backlinks, user engagement metrics, and content quality indicators. Google’s systems also look at expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness (E-A-T) when determining rankings, especially for topics related to health, finance, or other “your money or your life”

Ridam Khare is an SEO strategist with 7+ years of experience specializing in AI-driven content creation. He helps businesses scale high-quality blogs that rank, engage, and convert.



